본 절은 [TM1637]를 사용하기 위해 알아야 할 내용과 실습 방법에 대해 설명한다. 아두이노 TM1637 특징, 동작원리, 사양, 연결 핀 배열, 출력 값, 주의사항을 알아본다. 아두이노와 TM1637을 연결하고, 간단한 코딩으로 TM1637을 쉽게 실습할 수 있다.
목차
[디스플레이] 아두이노 TM1637-7세그먼트

TM1637-7세그먼트란?
TM1637 칩을 기반으로 하는 7세그먼트 디스플레이 모듈이다.

SS1 아두이노 센서 특징
TM1637-7세그먼트의 특징은 다음과 같다.
- 입력 전원 : 3.3~5.5V
- 사용 전류 : 30~80mA
- M2 고정홀 4개
TM1637-7세그먼트 구입하기
[TM1637-7세그먼트]는 알리익스프레스, 네이버 쇼핑몰, 아마존 등에서 센서를 구입할 수 있다

알리익스프레스에서다음과 같이 구입할 수 있다.
TM1637-7세그먼트 하드웨어 연결
다음과 같이 TM1637을 연결할 수 있다. 디스플레이 모듈에는 CLK 및 DIO인 2개의 신호 연결(및 2개의 전원 연결)이 있다. 이 핀은 Arduino의 모든 디지털 핀 쌍에 연결할 수 있다.
디스플레이에는 4개의 커넥터가 있다.
CLK - 클럭
DIO - 데이터
VCC - 전원 5v
GND - 접지
전원 참고: 안정적인 청정 전원은 회로 안정성에 중요하다. 고주파 업데이트 또는 애니메이션 시퀀스 중에 디스플레이 아티팩트가 표시되는 경우 TM1637과의 신호 타이밍 및 통신에 영향을 미치는 전력 변동이 발생할 수 있다. 이는 전력 조절이 없는 독립형 마이크로프로세서 애플리케이션에서 특히 그렇다. VCC 및 GND에 삽입된 극성화된 100uF 전해 커패시터는 스파이크를 부드럽게 만드는 데 도움이 될 수 있다.
소수 및 콜론: 일부 TM1637 디스플레이에는 디지털 시계에 사용되는 중간 콜론 LED가 장착되어 있지만 소수점은 없다. 일부 디스플레이에는 각 자릿수에 대한 소수점 LED가 있다. 일부는 둘 다 제공되지만 종종 소수점 LED가 연결되어 있지 않다. 이러한 추가 LED는 점 옆에 있는 숫자의 상위 비트(0x80)를 설정하여 활성화된다.
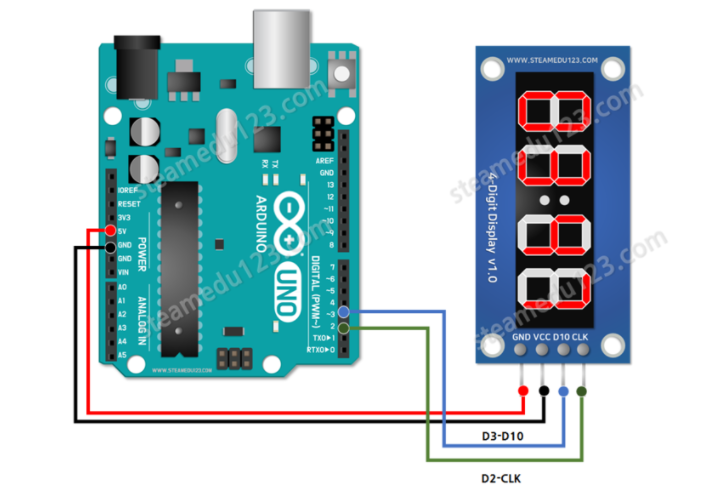
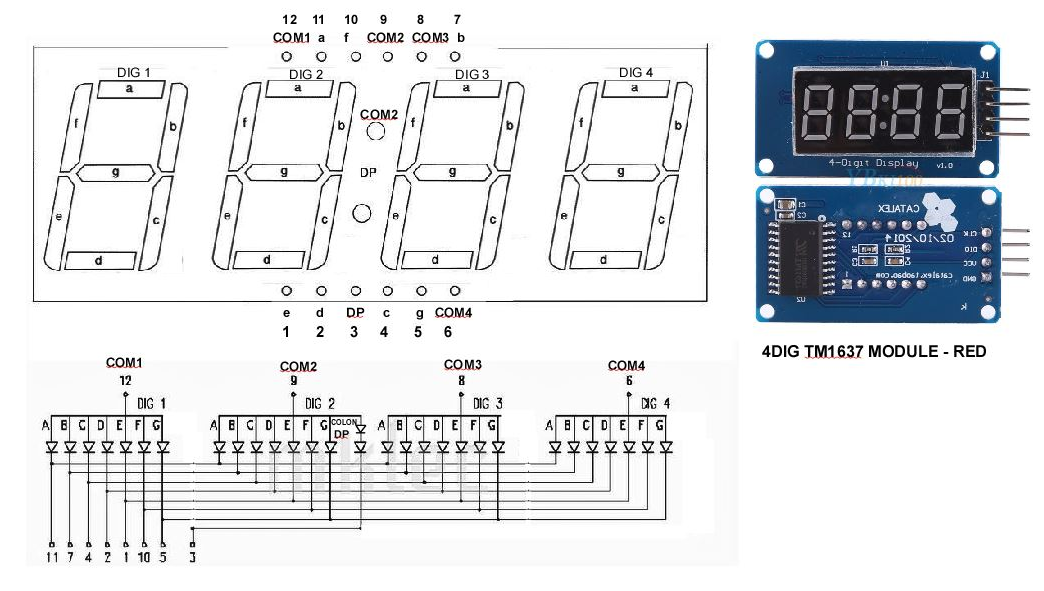
TM1637의 CLK는 아두이노의 D3 에 연결한다.
TM1637의 DIO는 아두이노의 D2 에 연결한다.
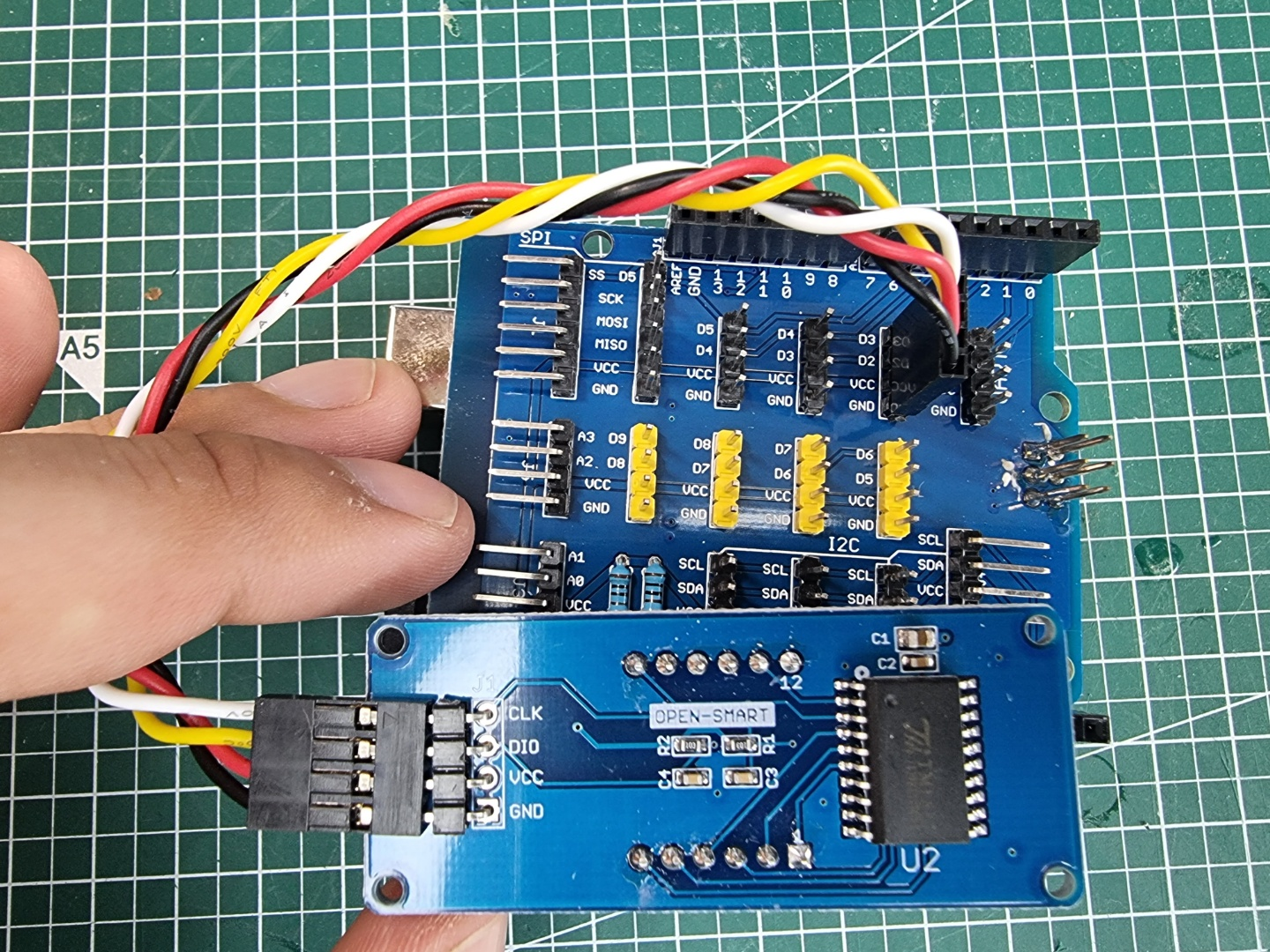
참고로 사용한 아두이노 쉴드는 다음과 같다.
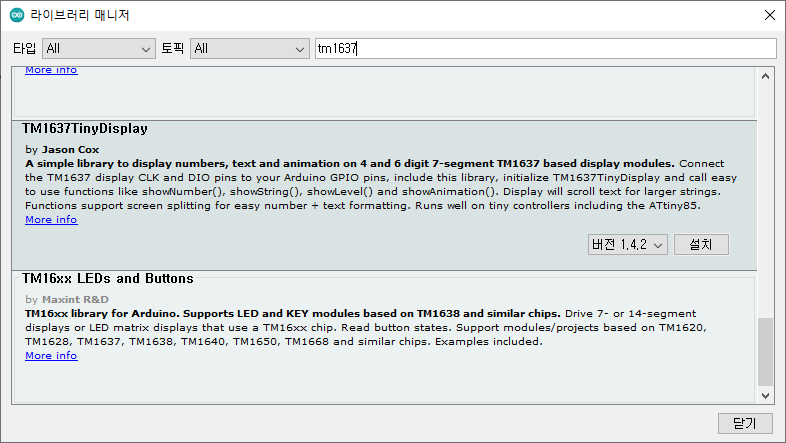
TM1637-7세그먼트 TM1637TinyDisplay 라이브러리
TM1637 을 사용하기 위해서는 라이브러리를 다운로드 해야 한다. TM1637 칩을 기반으로 하는 7세그먼트 디스플레이 모듈용 Arduino 라이브러리이다 .
TM1637-7세그먼트 소프트웨어 코딩
하드웨어 연결이 완료되면, 아두이노 IDE를 이용해 아두이노 센서 소스코드를 코딩할 수 있다.
코드는 다음과 같다.
// TM1637TinyDisplay TEST Sketch
// This is a test sketch for the Arduino TM1637TinyDisplay LED Display library
//
// Author: Jason A. Cox - @jasonacox - https://github.com/jasonacox
// Date: 2 July 2020
//
// Based on TM1637Display library at https://github.com/avishorp/TM1637
//
// Includes
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <TM1637TinyDisplay.h>
// Module connection pins (Digital Pins)
#define CLK 3
#define DIO 2
// The amount of time (in milliseconds) between tests
#define TEST_DELAY 1000
// Example of manually defining a display pattern
const uint8_t SEG_DONE[] = {
SEG_B | SEG_C | SEG_D | SEG_E | SEG_G, // d
SEG_A | SEG_B | SEG_C | SEG_D | SEG_E | SEG_F, // O
SEG_C | SEG_E | SEG_G, // n
SEG_A | SEG_D | SEG_E | SEG_F | SEG_G // E
};
// Example animation sequence for showAnimation() Test
// Built with 7-Segment Animator Tool
// https://jasonacox.github.io/TM1637TinyDisplay/examples/7-segment-animator.html
const uint8_t ANIMATION[12][4] = {
{ 0x08, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 0
{ 0x00, 0x08, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 1
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x08, 0x00 }, // Frame 2
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x08 }, // Frame 3
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x04 }, // Frame 4
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x02 }, // Frame 5
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01 }, // Frame 6
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00 }, // Frame 7
{ 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 8
{ 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 9
{ 0x20, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 10
{ 0x10, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 } // Frame 11
};
// To save RAM space, we can store the animation sequences in PROGMEM read-only flash memory.
// This requires using the showAnimation_P() function to read from PROGMEM memory space.
const uint8_t ANIMATION2[40][4] PROGMEM = {
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 0
{ 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 1
{ 0x40, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 2
{ 0x08, 0x40, 0x00, 0x01 }, // Frame 3
{ 0x00, 0x08, 0x01, 0x40 }, // Frame 4
{ 0x01, 0x00, 0x40, 0x08 }, // Frame 5
{ 0x40, 0x01, 0x08, 0x00 }, // Frame 6
{ 0x08, 0x40, 0x00, 0x01 }, // Frame 7
{ 0x00, 0x08, 0x01, 0x40 }, // Frame 8
{ 0x01, 0x01, 0x40, 0x08 }, // Frame 9
{ 0x40, 0x40, 0x09, 0x00 }, // Frame 10
{ 0x08, 0x08, 0x40, 0x01 }, // Frame 11
{ 0x01, 0x00, 0x08, 0x40 }, // Frame 12
{ 0x40, 0x01, 0x00, 0x08 }, // Frame 13
{ 0x08, 0x40, 0x01, 0x00 }, // Frame 14
{ 0x01, 0x09, 0x41, 0x01 }, // Frame 15
{ 0x40, 0x40, 0x48, 0x40 }, // Frame 16
{ 0x08, 0x08, 0x08, 0x08 }, // Frame 17
{ 0x1c, 0x1c, 0x1c, 0x1c }, // Frame 18
{ 0x3e, 0x3e, 0x3e, 0x3e }, // Frame 19
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 20
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 21
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 22
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 23
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 24
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 25
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 26
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 27
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 28
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 29
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 30
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 31
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 32
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 33
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 34
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 35
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }, // Frame 36
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 37
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f }, // Frame 38
{ 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f, 0x3f } // Frame 39
};
// Text string constants can be stored in PROGMEM read-only flash memory.
// This requires using the showString_P() function to read from PROGMEM memory space.
// PROGMEM space strings are globally defined.
const PROGMEM char FlashString[] = "Flash Test - 1234567890";
const PROGMEM char FlashString2[] = "good";
// Initialize TM1637TinyDisplay - 4 Digit Display
TM1637TinyDisplay display(CLK, DIO);
// Initialize TM1637TinyDisplay - 6 Digit Display
// TM1637TinyDisplay6 display(CLK, DIO);
void setup()
{
}
void loop()
{
int k;
uint8_t data[] = { 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff }; // Test Pattern - All
uint8_t blank[] = { 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }; // Test Pattern - Blank
display.setBrightness(BRIGHT_HIGH);
// Announce Testing
display.showString("Test");
delay(TEST_DELAY);
// All segments on
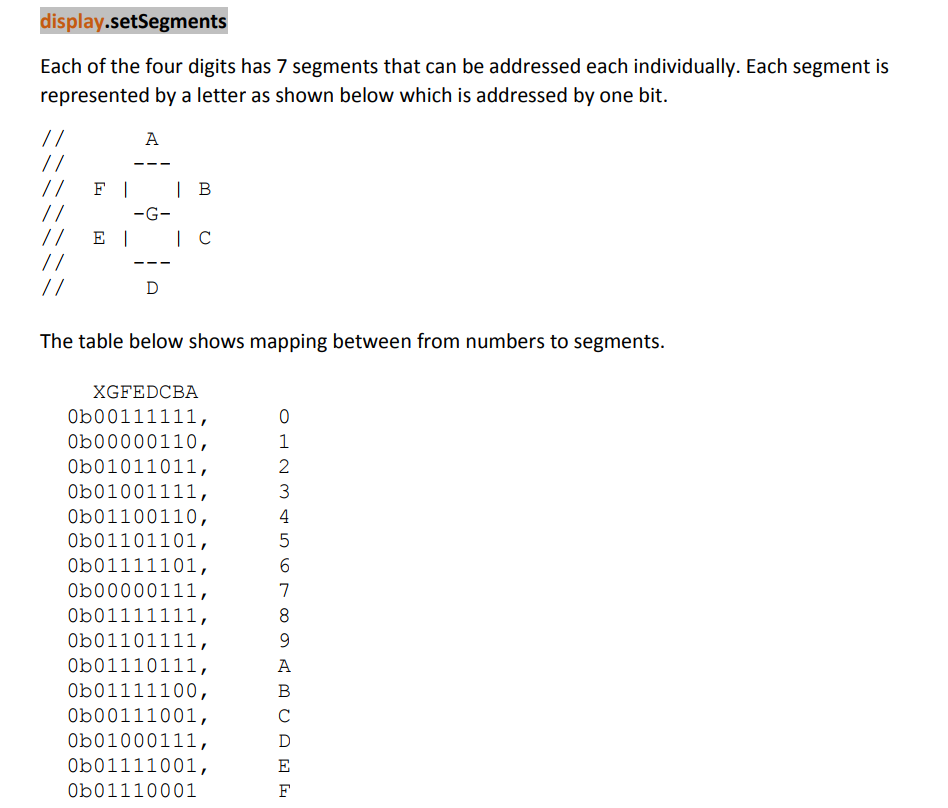
display.setSegments(data);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
// Test setting different digits
data[0] = display.encodeDigit(0);
data[1] = display.encodeDigit(1);
data[2] = display.encodeDigit(2);
data[3] = display.encodeDigit(3);
display.setSegments(data);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
// Test display splitting with position
display.clear();
display.setSegments(data + 2, 2, 2); // Length 2, Position 2
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.clear();
display.setSegments(data + 2, 2, 1); // Length 2, Position 1
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.clear();
display.setSegments(data + 1, 3, 1); // Length 3, Position 1
delay(TEST_DELAY);
// Test decimal numbers with/without leading zeros in different positions
display.showNumber(0, false); // Expect: ___0
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(0, true); // Expect: 0000
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(1, false); // Expect: ___1
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(1, true); // Expect: 0001
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(301, false); // Expect: _301
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(301, true); // Expect: 0301
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.clear();
display.showNumber(14, false, 2, 1); // Expect: _14_
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.clear();
display.showNumber(4, true, 2, 2); // Expect: __04
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(-1, false); // Expect: __-1
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(-12); // Expect: _-12
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(-999); // Expect: -999
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.clear();
display.showNumber(-5, false, 3, 0); // Expect: _-5_
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumberHex(0xf1af); // Expect: f1Af
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumberHex(0x2c); // Expect: __2C
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumberHex(0xd1, 0, true); // Expect: 00d1
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.clear();
display.showNumberHex(0xd1, 0, true, 2); // Expect: d1__
delay(TEST_DELAY);
// Floating point tests
display.showNumber(1.234); // Floating point number
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(1.234, 2); // Format to 2 decimal places
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(-1.234); // Negative floating point number
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(-0.5); // Zero prefix floating point number
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(0.4);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(1005.3);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(10005.3); // Overflow test
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(0.52345, 1);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showNumber(0.255, 2); // Test rounding up
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.clear();
display.showString("\xB0", 1, 3); // Test with suffix
display.showNumber(12.3, 4, 3, 0);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
for (int x = -100; x < 100; x = x + 1) { // Count
display.showNumber((float)x / 10.0);
}
// Test all the dots
for (k = 0; k <= 4; k++) {
display.showNumberDec(0, (0x80 >> k), true);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
}
// Test Brightness Levels
for (k = 0; k < 4; k++)
data[k] = 0xff;
for (k = 0; k < 7; k++) {
display.setBrightness(k);
display.setSegments(data);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
}
// Test Display On/Off
for (k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
display.setBrightness(7, false); // Turn off
display.setSegments(data);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.setBrightness(7, true); // Turn on
display.setSegments(data);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
}
// Test Horizontal Level Meter
for (int count = 0; count < 3; count++) {
for (int x = 0; x <= 100; x = x + 10) {
display.showLevel(x, true);
delay(20);
}
for (int x = 100; x > 0; x = x - 10) {
display.showLevel(x, true);
delay(20);
}
}
// Test Vertical Level Meter
for (int count = 0; count < 3; count++) {
for (int x = 0; x <= 100; x = x + 10) {
display.showLevel(x, false);
delay(20);
}
for (int x = 100; x > 0; x = x - 10) {
display.showLevel(x, false);
delay(20);
}
}
// Test Numbers and Strings Using Positions
display.clear();
char degree[] = "\xB0";
display.showString(degree, 1, 3); // Position 3 (right) and 1 char length
for (int x = -50; x < 150; x++) {
display.showNumber(x, false, 3, 0); // Postion 0 (left) and 3 char length
delay(10);
}
delay(TEST_DELAY);
// Test String Display
display.clear();
display.showString("String Test 1234"); // Test literal string
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.clear();
char stringb[10]; // Test dynamic string
sprintf(stringb, "25%cC", '\xB0'); // Display 25 + degree symbol + C
display.showString(stringb);
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.clear(); // Long string test
display.showString("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz.-=ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ");
delay(TEST_DELAY);
// Test Strings in PROGMEM flash memory
display.showString_P(FlashString);
delay(1000);
display.showString_P(FlashString2);
delay(1000);
// Animation Sequence Test in SRAM - Run 3 times
display.clear();
for (int count = 0; count < 3; count++) {
display.showAnimation(ANIMATION, FRAMES(ANIMATION), TIME_MS(10));
}
display.clear();
delay(TEST_DELAY);
// Animation Sequence Test in PROGMEM flash memory
display.clear();
display.showAnimation_P(ANIMATION2, FRAMES(ANIMATION2), TIME_MS(50));
// Done!
display.clear();
display.showString("The");
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.showString("End");
delay(TEST_DELAY);
display.setSegments(SEG_DONE);
delay(TEST_DELAY * 5);
}
TM1637-7세그먼트 동작확인
하드웨어 연결, 소프트웨어 코딩이 완료되면 다음과 같이 동작 화면을 확인할 수 있다.
------------------------------------------------------
개발환경 : WINDOWS 10
아두이노 IDE : 1.8.13
------------------------------------------------------
01 연결
- 아두이노와 PC 연결
- 아두이노 IDE 실행
- 메뉴 → 툴 → 보드:아두이노 UNO 확인
- 메뉴 → 스케치 → 확인/컴파일
02 컴파일 확인
스케치>확인/컴파일(CTRL+R) 를 선택해서 컴파일을 진행한다.
03 아두이노 우노 업로드
컴파일이 이상없이 완료되면 스케치>업로드(CTRL+U) 를 선택해서 컴파일 파일을 업로드 한다.
04 동작 확인
다음과 같이 동작을 확인할 수 있다.
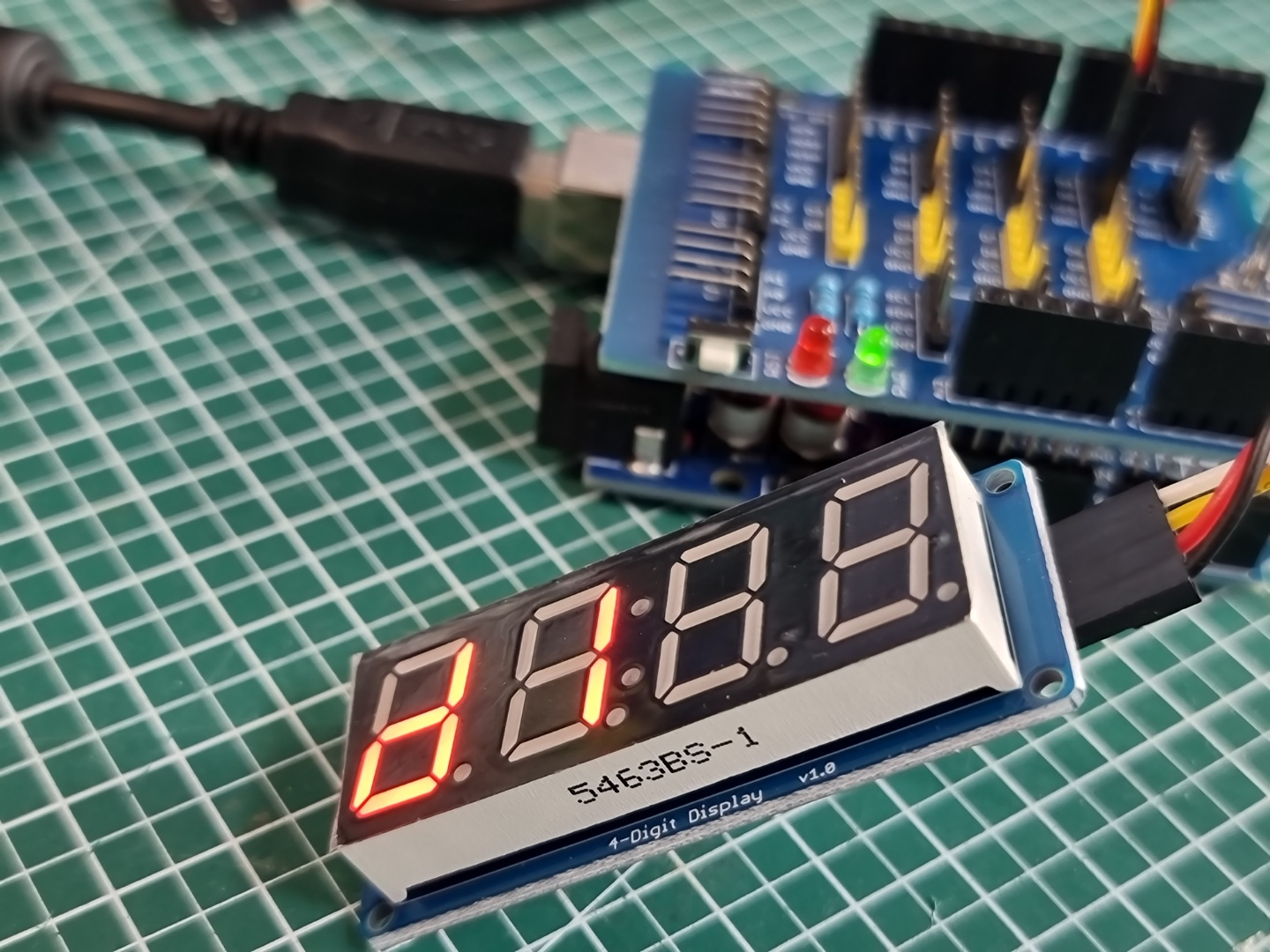
마무리
아두이노와 TM1637-7세그먼트를 연결하고, 간단한 코딩으로 모듈을 쉽게 실습할 수 있다.

모두의 아두이노 환경 센서 책
[모두의 아두이노 환경 센서] 책은 예스24, 인터넷 교보문고, 알라딘, 인터파크도서, 영풍문고, 반디앤루니스 , 도서11번가 등에서 구입할 수 있다. 이 책에서는 PMS7003, GP2Y1010AU0F, PPD42NS, SDS011 미세먼지 센서, DHT22 온습도 센서, MH-Z19B 이산화탄소 센서, ZE08-CH2O 포름알데히드 센서, CCS811 총휘발성유기화합물 TVOC, GDK101 방사선(감마선) 센서, MQ-131 오존(O3) 센서, MQ-7 일산화탄소, MICS-4514 이산화질소 센서, MICS-6814 암모니아 센서, DGS-SO2 아황산가스(SO2) 센서, BME280 기압 센서, GUVA-S12SD 자외선(UV) 센서, MD0550 기류 센서, QS-FS01 풍속 센서(Wind speed) 를 사용한다.
모두의 아두이노 환경 센서
아두이노와 센서로 내 건강을 지킬 수 있다!다양한 환경 센서를 실생활 프로젝트에 응용해보자!시중에 판매되고 있는 간이측정기도 센서로 값을 측정합니다. 똑같은 센서를 아두이노에 연결하
book.naver.com
'모두의 아두이노' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [아두이노] Keywish BLE-Nano for Arduino Nano V3.0 Mirco USB (0) | 2021.12.01 |
|---|---|
| [아두이노][쉴드] Data logger shield sd card and real time clock (0) | 2021.11.25 |
| [아두이노][쉴드] 아두이노 다기능 확장 쉴드 (0) | 2021.11.16 |
| [아두이노][센서] NEO-6M GPS 확장 쉴드 SD 카드 사용하기 (MicroSD) - ReadWrite 테스트 (0) | 2021.11.16 |
| [아두이노] 조이스틱 쉴드 (0) | 2021.11.11 |





댓글